SECURING THE RIGHTS OF AIR PASSENGERS
No. 1 in Europe: enforced over 500 million euros in compensation
No financial risk: we only charge our commission if successful
Transparent communication: we always keep you up-to date
We enforce your right to claim compensation and reimbursement in case of flight delay or cancellation!
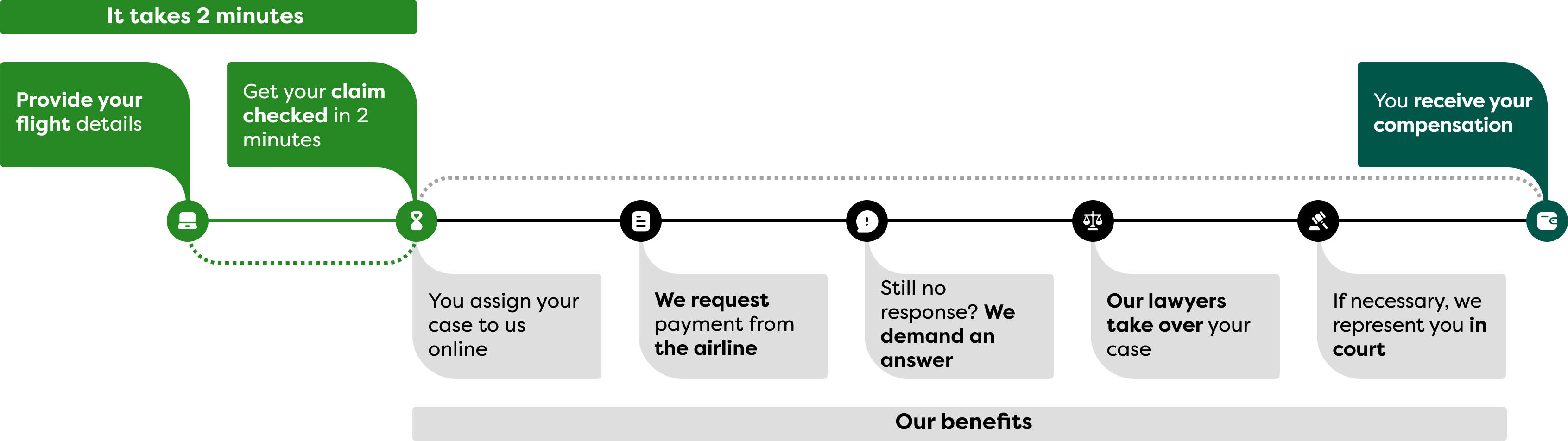
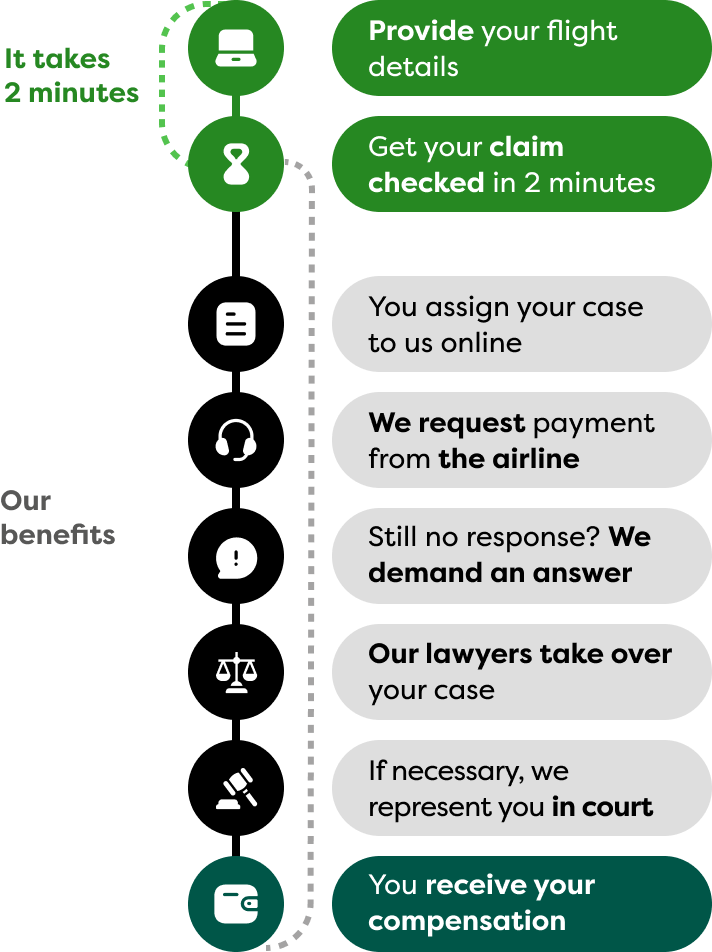
It’s this simple:
Simple, uncomplicated and time-saving – our legal experts enforce your rights!
Your quick and easy way to compensation
It’s that simple:

Known from TV and press
Secure your compensation now!
Check your claim fast and free of charge. We will enforce your rights for you!

Thousands of satisfied customers recommend Flightright
on Trustpilot
Frequently asked questions
People who want to take off on their long-awaited vacation or return home after their trip usually rely on the flight taking off as planned. Unfortunately, it happens all the time that flights are delayed, cancelled or a connecting flight is missed. The good news for affected passengers: in such cases, passengers have extensive rights under EU Air Passenger Rights Regulation 261/2004 and may be entitled to a ticket refund or compensation. This is at least a small compensation for the inconvenience caused. The EU Passenger Rights Regulation applies to flights departing from or arriving in the EU. In the latter case, the airline must also be based in the EU.
Flightright in numbers
€500 million paid out
99% success rate
14 years of expertise
Get your compensation now!
Check your claim now, quickly and for free. We enforce your rights for you!